Sampling And Data Collection Tips For Graduate Students
Discover practical data collection and sampling tips for graduate students working on dissertations. Learn research methods, tools, and expert advice to improve accuracy and save time.

When you’re working on your dissertation, one of the most important steps is gathering the right data. Without solid data, your research can quickly fall apart, no matter how well-written the rest of your work is. That’s why learning the right data collection tips early on can save you a lot of time and stress. If you’re feeling overwhelmed by where to start or what method to use, don’t worry—you’re not alone. Many graduate students struggle with this part of the process, but the good news is that it gets easier once you understand the basics.
Whether you’re working on surveys, interviews, experiments, or analyzing existing datasets, knowing how to collect your data in a clear and organized way is essential. Using effective data collection methods ensures that your results are reliable, which makes your dissertation stronger and more credible. Plus, choosing the right sampling strategy helps you focus your research and avoid unnecessary work. In this blog, we’ll walk you through the basics of sampling and data collection, share practical tips, and recommend tools that can help make your research process more efficient and accurate. For students who want extra support, platforms like FineWriters can provide expert help with everything from planning your sampling to refining your data collection process.
Understanding Sampling and Data Collection
Before you dive deep into your research, it’s important to understand the basics of sampling and data collection. These are two of the most critical parts of any dissertation or research project. Sampling is all about choosing the right group of people or items to study, while data collection focuses on gathering information from them in the most accurate way possible.
Getting these two steps right helps make sure your research is both manageable and meaningful. If you try to study too many people, especially in a large population, it can become overwhelming. On the other hand, if your sample is too small or not well-chosen, your results might not reflect reality. That’s why learning the right approach to data sampling and using smart data collection strategies is key.
What Is Data Sampling and Why Is It Important?

Data sampling is the process of selecting a smaller group from a larger population to represent the whole. Instead of gathering data from every single person or item—which can be time-consuming and expensive—you collect it from a sample and then draw conclusions based on that.
Sampling becomes especially important in research involving large populations, like nationwide surveys or broad user studies. If done properly, it helps you get accurate insights without needing to study everyone. Using the right sampling techniques also keeps your research focused, organized, and cost-effective, which is exactly what every graduate student needs. Understanding how to perform data sampling is essential for making your study both efficient and valid.
Introduction to Data Collection Techniques
Once you’ve figured out your sample, the next step is deciding how you’ll collect your data. There are several popular data collection techniques used in research, including surveys, interviews, observations, and experiments. Each method has its strengths, and the right one often depends on what kind of information you need.
For example, surveys are great for collecting large amounts of information quickly, while interviews are better for in-depth answers. No matter what you choose, one of the most useful data collection tips is to plan ahead—think about what questions you’re asking and how you’ll keep the data organized. Mastering how to collect data efficiently will help you reduce errors and improve your research quality.
Types of Data Sampling Methods
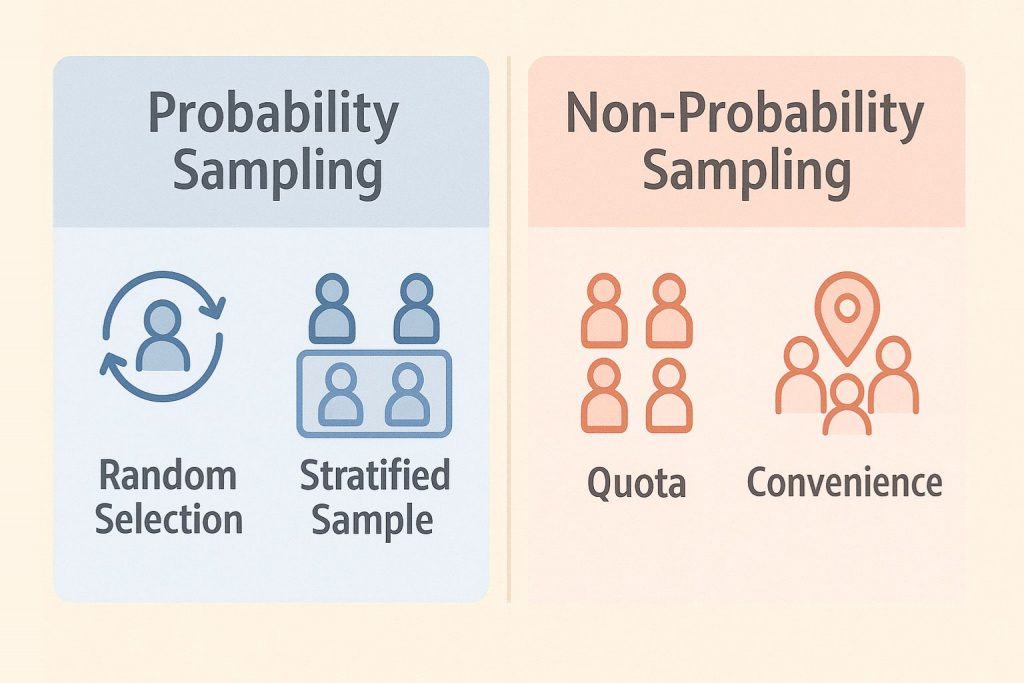
Understanding the different types of sampling methods can help you choose the right one for your research. There are two main categories: probability sampling and non-probability sampling. Each has its pros and cons, depending on your research goals, timeline, and resources.
Probability Sampling Methods
Probability sampling means every person or item in the population has a known chance of being selected. This approach is great for getting unbiased results and is often used in large-scale surveys and experiments. A few common sampling techniques for research include:
- Random sampling, where participants are chosen completely by chance.
- Systematic sampling, where you select every 10th or 20th person from a list (for example).
- Stratified sampling, where you divide the population into groups and randomly select from each group.
These data sampling methods for surveys help ensure your findings are accurate and can be generalized to the larger population. They’re especially helpful when working with lots of data or trying to be statistically precise.
Non-Probability Sampling Methods
Non-probability sampling doesn’t give everyone in the population an equal chance of being picked. It’s often faster and easier, which is why many students and researchers use it when time or access is limited.
Some useful data sampling techniques in this category include:
- Convenience sampling, where you use people who are easy to reach, like classmates or nearby participants.
- Quota sampling, where you target a certain number of people from specific groups.
- Purposive sampling, where you choose participants who have particular knowledge or experience related to your topic.
While these methods may not always give you results that apply to a whole population, they’re useful in small studies or when exploring specific topics more deeply.
Effective Data Collection Methods and Tools

When you’re working on your dissertation or any serious research project, having the right tools and methods makes a huge difference. The way you collect your data affects how accurate your results will be and how easy it is to analyze later. Fortunately, there are many data collection tools for businesses and researchers that can help you stay organized and efficient.
Tools and Software for Data Collection
There’s a wide variety of software available today to help you with collecting and managing data. For simple projects, Microsoft Excel is still a go-to tool for organizing and storing data. But if you’re dealing with more advanced statistics, SPSS, Stata, and SAS (Statistical Analysis System) are great options for running detailed analyses.
If you’re into programming, Python (using libraries like Pandas and NumPy) or R are excellent for custom data processing. RStudio is especially useful for students using R, as it provides a clean interface to work with. For visual learners, Tableau and Power BI are powerful platforms for creating interactive dashboards and visualizing trends. Math-heavy projects might benefit from using MATLAB.
All these tools are considered among the best data collection tools of 2025 for their flexibility, efficiency, and user-friendliness. The right one for you depends on your technical comfort level and the type of data you’re working with.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Dissertation
When it comes to sampling and data collection for a dissertation, you want to keep things simple but accurate. The method you choose should fit the goals of your research and the kind of questions you’re asking. For example, if you’re exploring opinions or experiences, interviews or open-ended surveys may be best. But if you’re working with numbers or trends, structured surveys or experiments might work better.
Using the right data collection techniques for research—like having clear questions, choosing the right participants, and using reliable tools—can help a lot in improving data collection accuracy. Planning everything out ahead of time and doing small test runs before full data collection can save you from major mistakes. Choosing carefully now means less stress when you’re writing your analysis later, and it sets a strong foundation for your overall dissertation writing process.
Practical Data Collection Tips for Graduate Students

Collecting data for a dissertation isn’t just about picking a method—it’s about doing it well. Every step, from writing survey questions to organizing your files, matters more than you think. A bit of planning and care can make your work more reliable and save you hours down the road.
Tips for Collecting Accurate Data
Accuracy is everything when it comes to research. One of the best tips for collecting accurate data is to be super clear about what you’re measuring. Vague questions or messy forms will lead to messy results. Always double-check your tools, whether that’s an online survey, a spreadsheet, or a physical form.
To collect data efficiently, consider using software that fits your needs—Excel for small projects, or something like SPSS or R for more complex work. Also, don’t forget to back up your data. Losing files is one of the most frustrating mistakes students face.
Lastly, stick to data collection best practices: label everything clearly, keep your process consistent, and check your data for errors regularly. It’s not exciting, but it’s worth it.
Data Collection Tips for Surveys and Interviews

Surveys and interviews are two of the most common tools used by students. For surveys, the best data collection tips for surveys include keeping your questions short, avoiding confusing language, and always testing your form on a few people before going live.
For interviews, prepare a list of questions in advance, but stay flexible—you want honest answers, not a script. In both cases, having a strategy helps. For example, using sampling techniques for research, you might choose to focus on a specific age group, profession, or interest group to keep your study focused.
Let’s say you’re studying social media habits among college students. A survey might work best with a random sample from different classes, while an interview could help you explore habits in more depth. The method depends on your research goals, but smart planning makes all the difference.
Data Collection Challenges and How to Overcome Them
No research project goes perfectly. From unclear answers to missing files, things can (and often do) go wrong. But knowing the common issues ahead of time can help you plan better and avoid the worst of the mess.
Common Pitfalls in Sampling and Collection
One major challenge is bias, which can sneak into your research without you realizing it. If your sample is too small or too similar, your findings may not apply to a wider group. This is where good data sampling strategies come in, helping you build a more balanced group.
Another issue is incomplete data—people skipping questions, quitting halfway, or giving vague answers. Poorly framed surveys with confusing questions can make this worse. Also, it’s common to lose track of your data if you’re not organized from the beginning. Avoid the headache by having a system in place before you collect anything.
Solutions and Pro Tips
To overcome these challenges, start by designing clear, focused questions. Run a pilot test with a few participants to catch any confusing parts. Use software like Excel, SPSS, or Python to help organize your data and flag missing or unusual entries.
Document everything—from how you selected your sample to how you handled skipped questions. This keeps your process transparent and helps later when writing your methodology section. Regularly back up your files and set reminders to review your progress. A little structure goes a long way in keeping your data clean and reliable.
Expert Advice and Tools for Students

Getting help during your research journey can make everything smoother, especially when it comes to data. From figuring out your sample size to choosing the right method for collecting data, expert advice can save you from common mistakes and confusion. Thankfully, students today have access to platforms, tools, and templates that can make the process easier and more efficient. Using ready-made dashboards, analysis templates, or even scripts can help you avoid starting from scratch. And if you’re not sure where to begin, getting one-on-one support with data sampling, data collection, and organizing your findings can be a game-changer—all tailored to your dissertation needs.
How FineWriters Helps With Data-Driven Dissertations
If you’re feeling stuck with your research, you can count on personalised support that truly makes a difference. Whether you’re trying to figure out your sampling techniques or need guidance on the best way to collect your data, their team walks you through the process step by step. They assist graduate students in planning their methodology, choosing the right tools, and ensuring the data collected is accurate and ready for analysis. You’re not just getting writing assistance—you’re also receiving practical help to build a strong, data-driven dissertation that meets high academic standards. If you’re wondering what comes next after data collection, check out How To Structure Your Dissertation? A Step By Step Guide to make sure you’re on track for a clear and organised final submission.
Recommended Software and Templates
There are so many tools out there to make your research easier. If you’re using Tableau, you’ll find tons of ready-to-use dashboards that let you plug in your data and see trends instantly. For coding-based projects, pre-built scripts in R or Python (using Pandas or NumPy) can help automate common analysis tasks. These are great if you want to save time and reduce manual errors. Templates in Excel and SPSS can also guide you in setting up your data sheets correctly. These resources are all about helping you stay organized and focused, especially when you’re deep into dissertation work.
Conclusion
Mastering sampling and data collection is one of the most valuable skills a graduate student can develop. It doesn’t just make your research stronger—it also helps you build confidence in your own process. Whether you’re running a large survey or doing in-depth interviews, using the right data collection tips, tools, and planning methods can take your dissertation to the next level.
Remember to keep your methods simple, your data clean, and your sample well-chosen. Following data collection best practices and using the right sampling techniques for research can save you time and help avoid common problems down the line. Don’t be afraid to lean on helpful resources either—you’re not expected to do it all alone.
If you’re looking for expert guidance tailored specifically for graduate students, FineWriters is a great place to start. They offer practical, research-focused support to help you confidently navigate every stage of your dissertation, from planning your sample to analyzing your data with accuracy.
